Construction waste management is a critical aspect of sustainable construction practices, necessitating efficient methods for processing and recycling waste materials. Within construction waste crushing plants, the presence of light density particles poses challenges to effective waste separation and resource recovery. Wind sifters offer a specialized solution to this issue by enabling the removal of light density particles, thereby optimizing the recycling process.

Wind Sifter in Construction Waste Crushing Plant
Light Density Particles in Construction Waste
Construction waste comprises a diverse array of materials, including but not limited to:
- Polystyrene foam: Used in insulation and packaging materials, polystyrene foam is lightweight and voluminous, making it challenging to process and recycle efficiently.
- Plastic debris: Various types of plastic waste, such as packaging materials, bottles, and containers, contribute to the light density fraction of construction waste.
- Paper and cardboard: Cardboard boxes, packaging materials, and paper waste generated during construction activities add to the light density particles present in waste streams.
- Textile fibers: Discarded textiles from construction sites, such as protective clothing and fabric scraps, constitute another component of light density particles.
Challenges posed by these light density particles include increased transportation costs, reduced landfill space, and environmental pollution if not managed effectively.
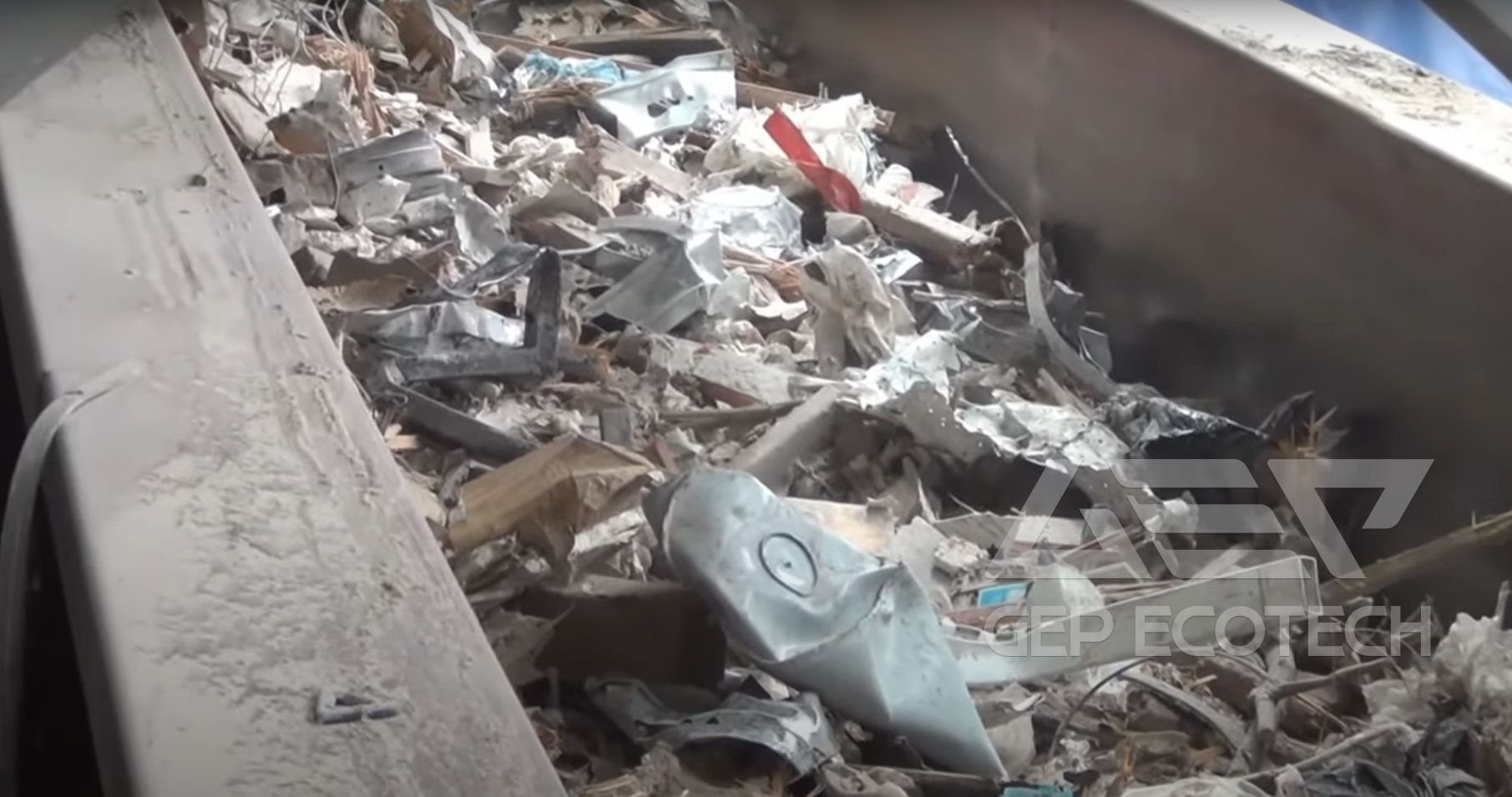

Construction Waste
Role of Wind Sifters in Removal of Light Density Particles
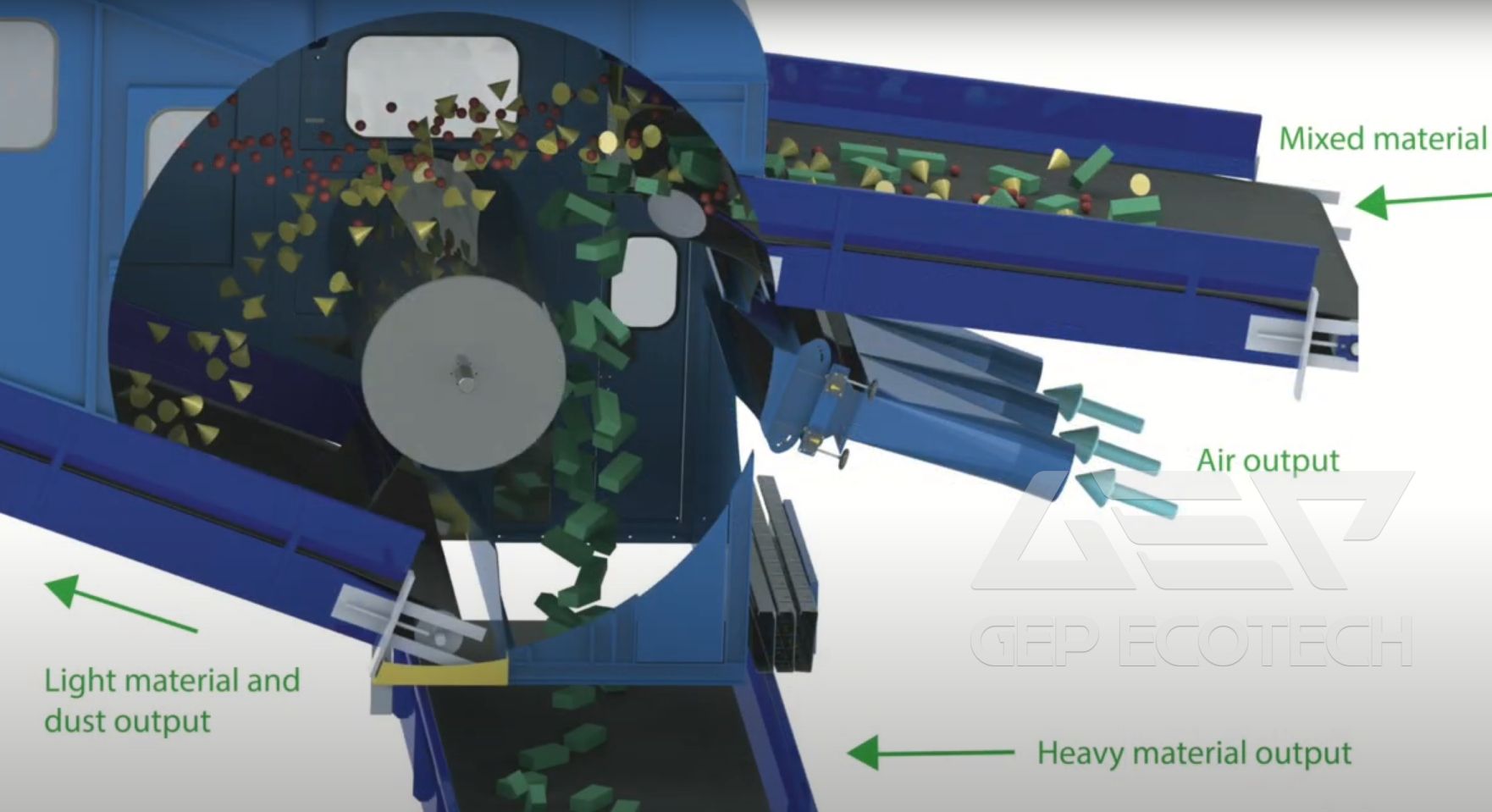
Wind sifters, also known as air classifiers or air separators, utilize airflow and differential particle settling velocities to separate materials based on their density and aerodynamic properties. The operational principle of wind sifters involves the following steps:
- Material Feeding: Construction waste materials are fed into the wind sifter system, where they undergo initial screening to remove oversized particles and debris.
- Airflow Distribution: Controlled airflow is introduced into the sifter chamber, creating a turbulent environment that facilitates the separation of materials based on their density.
- Particle Separation: Light density particles, such as foam, plastic, paper, and textile fibers, are carried upward by the airflow, while heavier materials, such as concrete, bricks, and metals, settle downward due to gravity.
- Collection and Discharge: Separated materials are collected in designated bins or conveyors for further processing or recycling, while residual waste is discharged for appropriate disposal.
Wind sifters play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of construction waste management practices by enabling the removal of light density particles from waste streams. Their ability to separate materials based on density promotes resource recovery, improves product quality, and reduces environmental impact, making them indispensable tools in modern construction waste crushing plants. Embracing innovative technologies like wind sifters is essential for advancing towards a circular economy and achieving long-term sustainability goals in the construction industry.