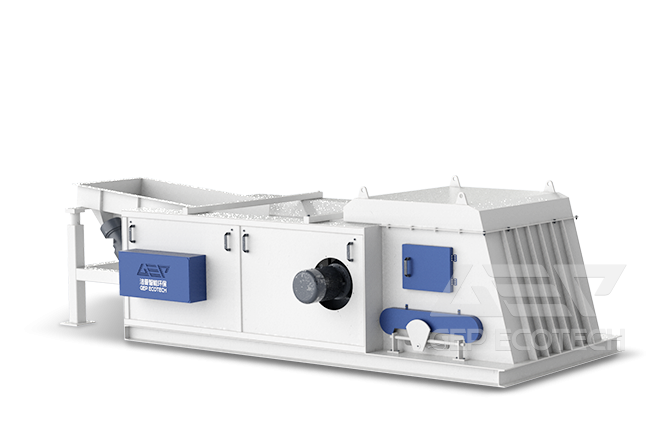
Flammable metal sponges, such as magnesium, sodium, and titanium sponges, are used in various industrial applications for their lightweight and reactive properties. These materials, however, pose significant challenges when it comes to size reduction due to their high reactivity, especially when finely divided. The risk of combustion, explosion, and even catastrophic failure is particularly acute when the metal sponge is processed using traditional mechanical methods like shredding. To safely and efficiently reduce the size of these materials, specialized size-reducing shredders have been developed. These machines are designed to handle the specific risks associated with flammable metals while maintaining processing efficiency.
This article explores the function, challenges, safety features, and best practices involved in using size-reducing shredders for flammable metal sponge materials.
What is Flammable Metal Sponge?
Flammable metal sponges refer to highly porous forms of metals that have a large surface area, making them reactive, especially when finely powdered. Some common types of flammable metal sponges include:
- Magnesium Sponge: A lightweight, highly reactive metal, used extensively in aerospace, automotive, and pyrotechnics. Magnesium sponge is particularly prone to ignition and combustion when ground into fine particles.
- Titanium Sponge: Used in aerospace and medical implants, titanium sponge is less reactive than magnesium but still presents handling and size reduction challenges, especially when small particles are produced.
- Sodium Sponge: Extremely reactive with moisture and oxygen, sodium sponge requires extreme caution during handling, particularly during size-reducing processes.
Because of their high surface area and chemical reactivity, these sponges are prone to catching fire when exposed to heat, friction, or even air in some cases, particularly when processed into fine particles.

Challenges in Size Reduction of Flammable Metal Sponge
The process of size reduction of flammable metal sponge materials involves breaking large chunks of metal into smaller, more manageable sizes or powders. However, this process comes with several significant challenges:
- Combustion Risk: Flammable metal sponges can spontaneously ignite when exposed to heat or friction, especially when finely divided. The fine dust produced during size reduction can create a highly explosive environment.
- Explosion Risk: When the dust generated during shredding is suspended in the air, it can form a combustible dust cloud. If this dust cloud is ignited, it can cause an explosion with catastrophic consequences.
- Friction and Heat Generation: Shredding or cutting metals generates heat due to mechanical friction, which can further increase the risk of ignition, particularly for metals like magnesium and sodium.
Given these challenges, size-reducing machines designed for flammable metal sponges need to incorporate specific safety features to reduce the risk of ignition and ensure safe operation.
The Role of Size-Reducing Shredders
Shredders are widely used in materials processing to reduce large pieces of metal into smaller, more manageable sizes. For flammable metal sponges, shredders offer the advantage of breaking down large chunks of metal without requiring the extreme heat generation that other methods, like grinding, might produce. However, the machinery must be designed to accommodate the unique safety needs of processing reactive materials.
Shredders used for flammable metal sponge typically employ cutting or tearing mechanisms to reduce the size of the material. These devices are generally designed with special considerations to mitigate the risks associated with flammable metal processing.
Types of Size-Reducing Shredders for Flammable Metal Sponge
Single-Shaft Shredders
Single-shaft shredders use a single rotating shaft with multiple sharp blades to cut the material into smaller pieces. The design is simple and efficient, making it suitable for reducing larger metal sponges into smaller, more uniform sizes.
Advantages:
- Can handle relatively large chunks of sponge.
- More energy-efficient than other methods.
- Easier to maintain and operate.
Safety Features:
- Explosion-proof enclosures to prevent the ignition of fine dust.
- Low-speed operation to minimize the generation of heat and friction.
- Continuous monitoring of temperature to prevent overheating.
Twin-Shaft Shredders
Twin-shaft shredders use two counter-rotating shafts with blades or hooks to shred materials. These machines are often used for tougher, more dense materials, and they offer more consistent cutting performance.

Advantages:
- Better for shredding tougher, denser materials than single-shaft models.
- More controlled size reduction, which can help maintain a safer particle size.
Safety Features:
- Inert gas purging to prevent exposure to oxygen.
- Specialized seals to contain any flammable dust within the shredder chamber.
- Dust extraction systems to reduce the accumulation of combustible dust.
Hammer Mills
Hammer mills use rotating hammers to strike and break apart materials. The impact forces break the material into smaller particles, and the shredded material is then passed through a screen for uniformity.
Advantages:
- Suitable for reducing large volumes of metal sponge material quickly.
- Can process various materials with different hardness levels.
Safety Features:
- Enclosed chambers to prevent sparks and heat from escaping.
- Dust suppression or collection systems to capture fine particles.
- Proper grounding and anti-static features to minimize the risk of sparking.
Shredding Systems with Inert Atmosphere
Some shredding systems for flammable metal sponge use an inert atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen or argon) within the processing chamber. This setup prevents the metal from coming into contact with oxygen, thereby reducing the risk of ignition during the shredding process.
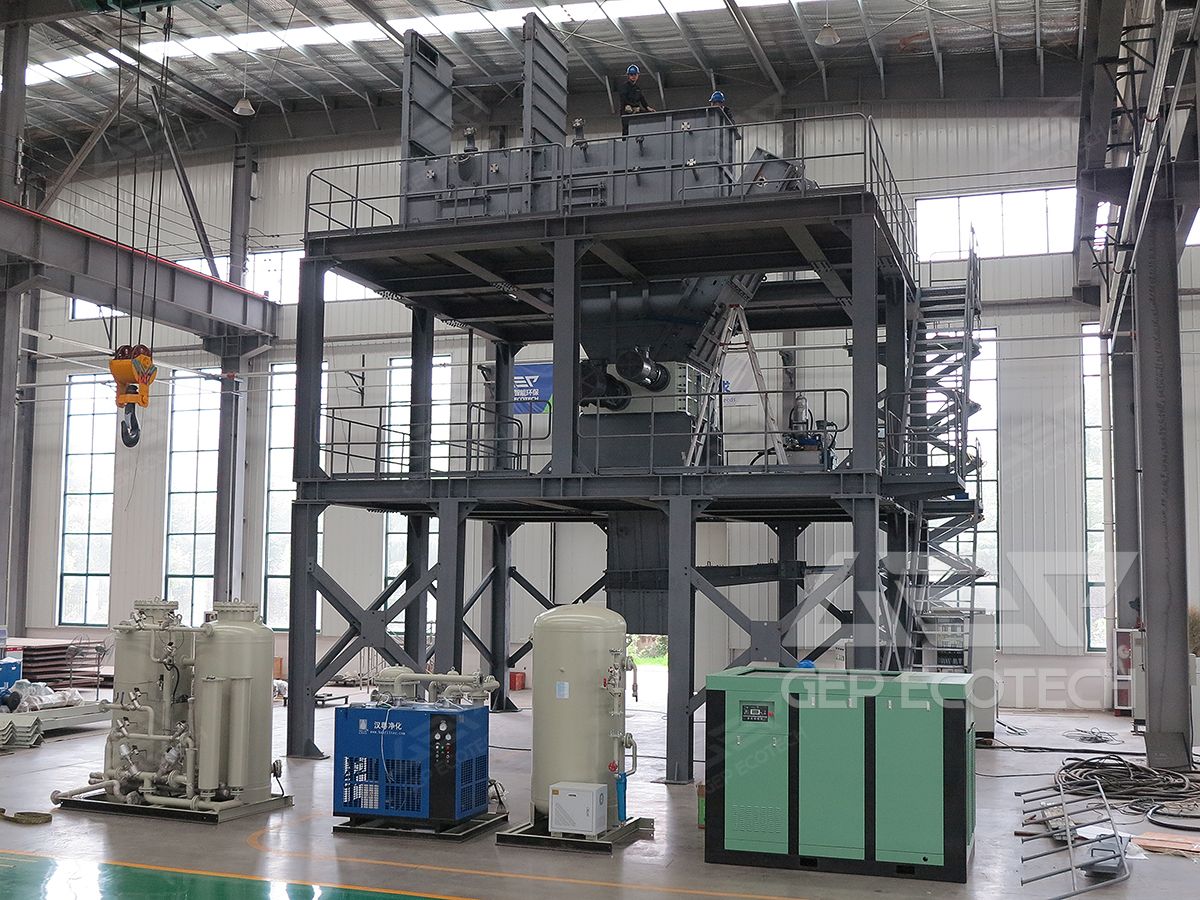

Advantages:
- The inert atmosphere significantly reduces the risk of combustion.
- Prevents oxidation of the metal during size reduction, which could affect the quality of the shredded material.
Safety Features:
- Continuous inert gas flow to maintain the proper atmosphere.
- Explosion-proof sealing to prevent any gas leaks.
- Temperature and pressure monitoring to maintain the stability of the inert environment.
Safety Measures in Shredding Flammable Metal Sponge
The safety of the shredding process is paramount when dealing with highly reactive materials. Several key safety measures and best practices must be implemented to ensure the safe operation of size-reducing shredders for flammable metal sponge materials:
- Explosion-Proof Equipment: Shredding machines used for flammable metal sponges must be explosion-proof and capable of containing any potential sparks or heat generated during operation. Explosion-proof motors, enclosures, and electrical systems are essential.
- Inert Gas Environments: Many size-reducing machines for reactive metals operate in an inert atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxygen from interacting with the metal and triggering ignition. This is especially important for metals like magnesium and sodium, which react violently with air.
- Dust Collection and Suppression: Efficient dust collection systems must be in place to capture fine metal particles generated during the shredding process. Accumulated dust can create an explosive environment, so it is critical to keep airborne dust levels low and remove dust from the processing area immediately.
- Low-Speed and Controlled Operation: Shredders for flammable metal sponges are often designed to operate at lower speeds to reduce friction and heat buildup. Additionally, monitoring systems can track the temperature inside the shredding chamber to prevent overheating.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Maintenance is essential to ensure that shredders remain in good working order. Routine checks for wear and tear on blades, seals, and electrical components should be conducted to prevent equipment failure.
- Operator Training: Workers handling flammable metal sponges should receive thorough training in the proper operation of size-reducing machinery. They should also be trained to handle emergencies, including the safe response to fires, explosions, or other incidents.
Size-reducing shredders are essential tools for processing flammable metal sponges, offering a safe and efficient way to break down large chunks of highly reactive materials into smaller, more manageable pieces. While these machines provide numerous advantages, including increased surface area for chemical reactions or easier handling, they must be designed with safety as a top priority.
By using shredders equipped with explosion-proof systems, inert gas environments, and effective dust collection, industries can safely process flammable metal sponges without sacrificing efficiency. As advancements in shredding technology continue, it is likely that these machines will become even more refined, offering better control over size reduction while minimizing risk to workers and facilities.