With the rapid development of science and technology, the frequency of updating electronic products is accelerating, followed by the increasing number of electronic waste and the aggravation of the environmental burden. The renewable resources available in electronic waste include steel, nonferrous metals, plastics, and of course, there are also toxic and harmful substances, such as lead in welding, cadmium in resistors/semiconductors, mercury in printed circuit boards (PCBs), chromium in metal coatings, lead/mercury/cadmium in batteries, and beryllium in motherboards. How to treat them innocuously and as resources is a difficult problem that needs to be solved urgently.

GEP's electronic waste disposal production line can effectively solve such problems. The electronic waste is first broken and separated using a dedicated shredder for electronic waste, and then separated by an magnetic separator and eddy current separator. Plastic and different types of metals are transported to different areas, where useful metals are recycled and harmful metals are collectively disposed of harmlessly.
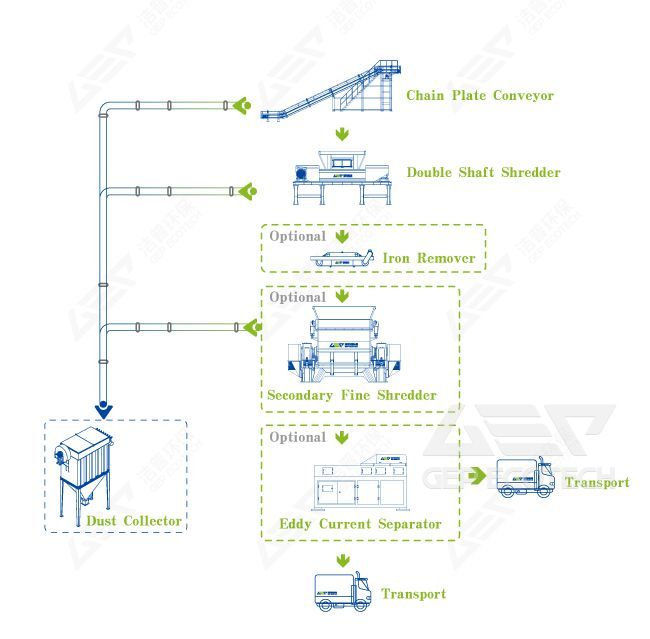
This production line has a front-end automatic decomposition function, which can achieve precise decomposition from simple disassembly to product refinement. Equipment such as magnetic separator and eddy current separator are used to sort and dispose of the broken metal materials, further improving the added value of electronic waste, effectively promoting the recycling of resources, and effectively eliminating environmental hazards of hazardous substances.