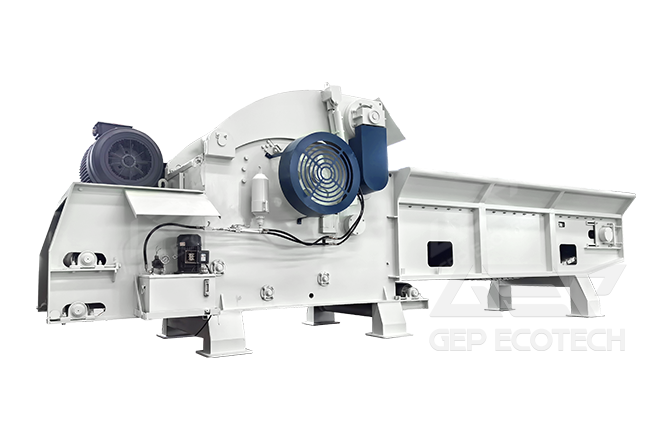
The main sources of textile waste are waste textiles (such as waste silk, residual materials, scraps, etc. in the textile manufacturing process) and old textiles (old clothing, bedding, curtains, carpets, etc.).
The calorific value of waste textile is around 4000-7000 kcal, and the average calorific value is basically around 4300 kcal. The volatile matter is about 80-90% (pulverized coal is about 27%), the ash content is about 1-6% (pulverized coal is about 15%), and the moisture content is about 4% (pulverized coal is about 8%). Compared with pulverized coal, waste textile has high volatile content, low ash content, low moisture content, and considerable calorific value, so it has good potential as an alternative fuel.

Technical Routes for Using Waste Textiles as Cement Kilns Alternative Fuel
In recent years, as rising energy prices have put greater cost pressure on companies, more and more cement companies have begun to explore the use of alternative fuels. Waste textile has become the first choice of many companies because of its characteristics and potential.
Currently known technical routes include:
- Simple storage + shredding pretreatment + transporting feed materials into the decomposition furnace;
- The incoming materials are transported and fed directly into the decomposition furnace;
- Utilize existing co-processing facilities to coordinate pretreatment (or existing) + pre-combustion furnace + decomposition furnace.
These routes have different heat utilization efficiencies for waste textile, but they have all achieved good fuel substitution effects and have promising prospects.
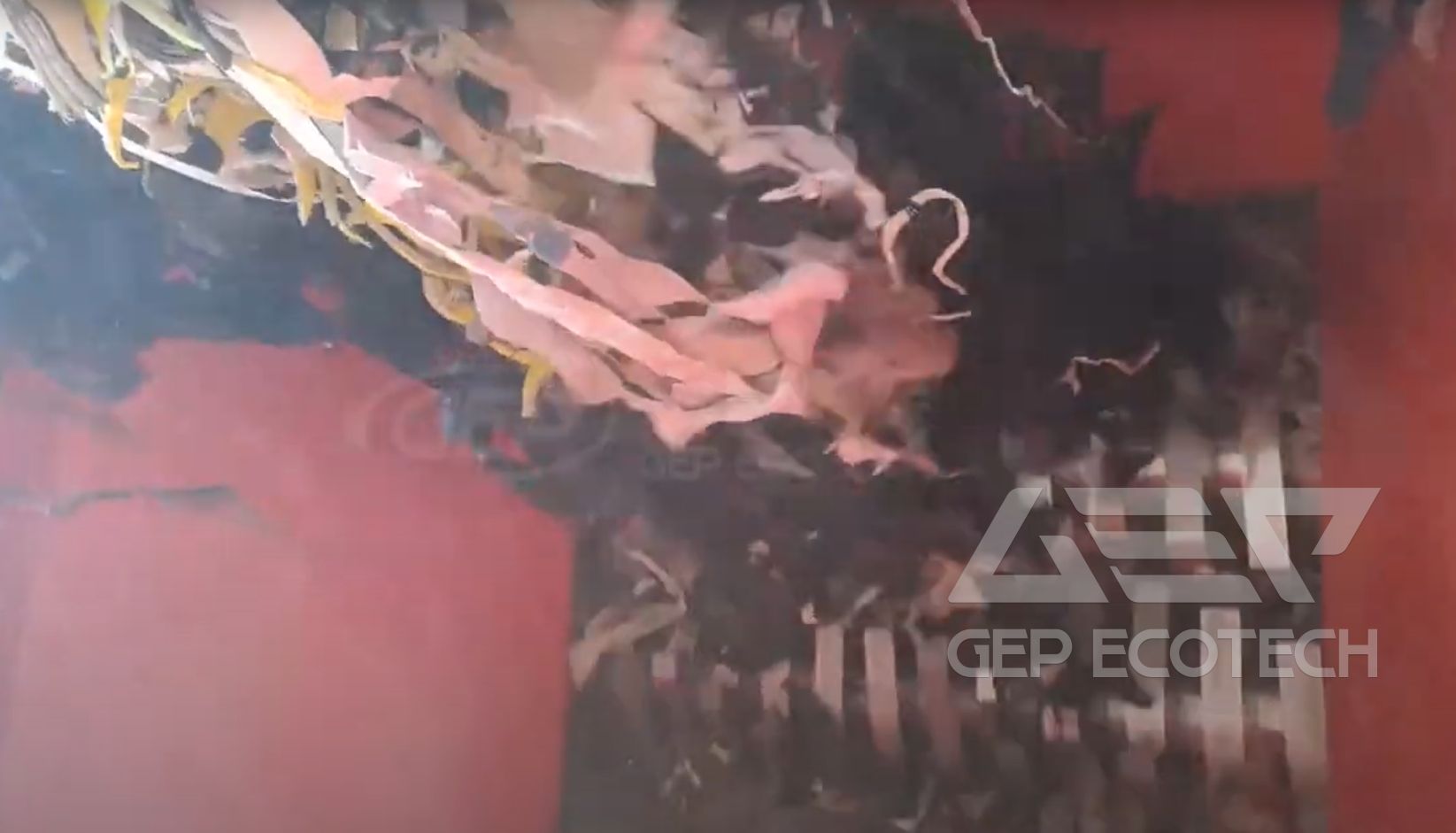

Textile Shredding Pretreatment
Key Points of Using Waste Textiles as Cement Kilns Alternative Fuel
1. Morphological properties
The form, calorific value, moisture content, etc. of waste textiles fluctuate greatly. If no control is carried out, the combustion will fluctuate greatly after entering the decomposition furnace. There will be problems such as an increase in the temperature fluctuation range of the decomposition furnace, incomplete combustion, and an increase in reducing gas. Therefore, when cement plants use waste textile, they should pursue a stable source of materials to reduce fluctuations in calorific value, moisture, etc. At the same time, it is necessary to carry out pretreatment based on the actual situation of the factory, and precise and stable metering and feeding measures to stabilize its properties and feeding volume and reduce the impact of fluctuations on energy consumption and production quality.
2.Safety
Waste textileis relatively fluffy, with a bulk density of less than 0.2 tons/cubic meter. There is a greater risk of spontaneous combustion during storage. When storing waste textiles, cement plants need to strengthen monitoring of spontaneous combustion risks through thermal monitoring and other measures and prepare fire-fighting measures. Many domestic cement companies that use waste textiles have had spontaneous combustion accidents, but fortunately they were all disposed of in a timely manner.
Waste textile itself and its processing will produce a lot of floc-like dust, which is quite different from the inorganic granular dust previously processed by cement plants. These lint-packed dusts have a greater risk of explosion, and it is difficult for the original dust collection facilities to effectively collect dust. Cement companies should learn from the dust removal technology, equipment and risks of the textile industry.
3. Hazardous substances
In waste textiles, the chlorine content is between 0.2-0.6%, because the national cement standard chloride ion limit is 0.06%. The impact of chloride ions brought by waste textiles is still great. If the chloride ions in the raw materials are high or other chlorine-containing wastes are co-processed, the use of waste textiles will be limited. Cement companies need to add chlorine removal facilities based on actual needs.
The heavy metals and sulfur content in waste textiles are extremely low and have basically no impact on cement production.
4. Fuel replacement rate
Waste textiles of different properties and forms enter the decomposition furnace through different technical routes, and the fuel substitution effects are also quite different. But basically it can achieve the fuel substitution effect of 1 ton of waste textile replacing 0.7-0.9 tons of coal. Cement plants should pursue the best burnout rate of waste textile and make full use of its heat energy in appropriate areas to improve energy conversion efficiency.
5. Smoke emissions
No matter how the waste is pretreated, it is difficult to achieve the properties of pulverized coal, which determines that some waste will be burned in useless areas and burned incompletely. This can lead to an increase in carbon monoxide in the system's flue gases. If high concentrations of carbon monoxide appear in areas where ammonia is out of stock, it will compete with nitrogen oxides to reduce ammonia, thereby increasing the amount of ammonia used. It will also lead to the reduction of calcium sulfate, increasing the risk of sulfur oxide emissions and crusting and clogging.
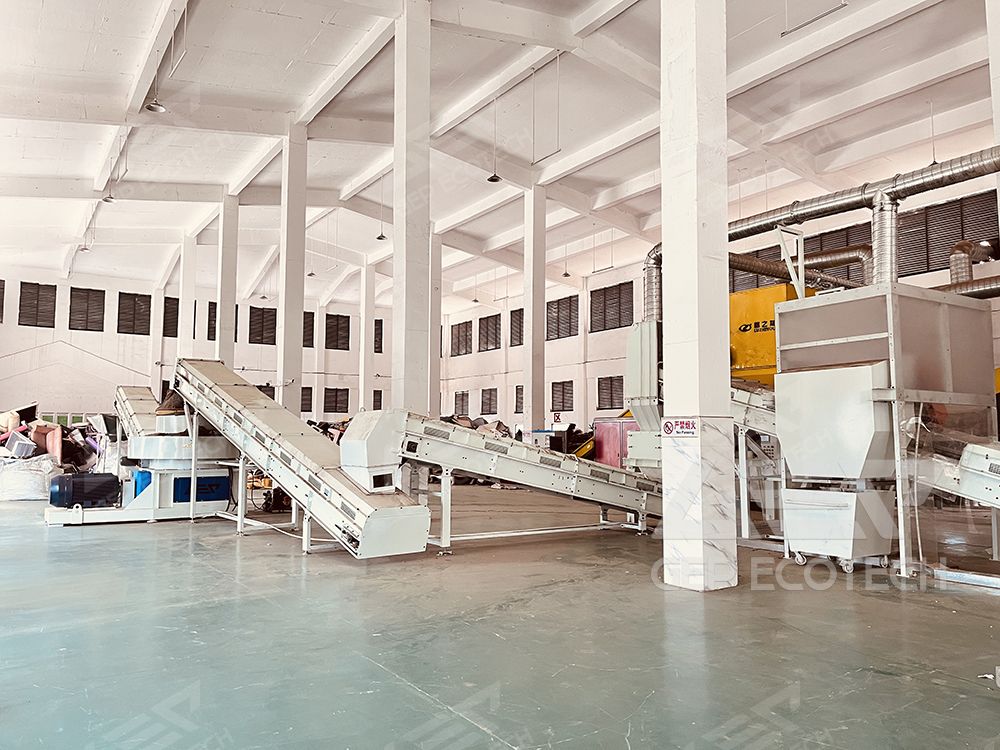

GEP ECOTECH Waste Textile Alternative Fuel Production Line
GEP has advanced technology and equipment in the production of waste textile alternative fuels to help cement kiln companies reduce costs and increase efficiency. For more cement kiln alternative fuel issues, you are welcome to contact us to discuss.