The coconut palm is one of the most useful tropical trees and is used for food, beverage, shelter, animal feed, and is grown industrially for the edible and highly saturated oil contained in the flesh of its fruits. The tree can survive 50 years without needing much attention and the fruits drop throughout the year. The nut has a smooth epidermis over a fibrous mesocarp (husk) that covers the hard endocarp (shell). A thin brown layer (testa) separates the shell from the endosperm (kernel, flesh, meat), which is approximately 1-2 cm thick. A cavity within the kernel contains the coconut water.
The husk and shells can be used for fuel and are a source of charcoal. Activated carbon manufactured from coconut shell is considered extremely effective for the removal of impurities. Coconut husk has high amount of lignin and cellulose, and that is why it has a high calorific value of 18.62MJ/kg. The chemical composition of coconut husks consists of cellulose, lignin, pyroligneous acid, gas, charcoal, tar, tannin, and potassium. The predominant use of coconut husks is in direct combustion in order to make charcoal, otherwise husks are simply thrown away. Coconut husk can be transformed into a value-added fuel source which can replace wood and other traditional fuel sources. In terms of the availability and costs of coconut husks, they have good potential for use in power plants.
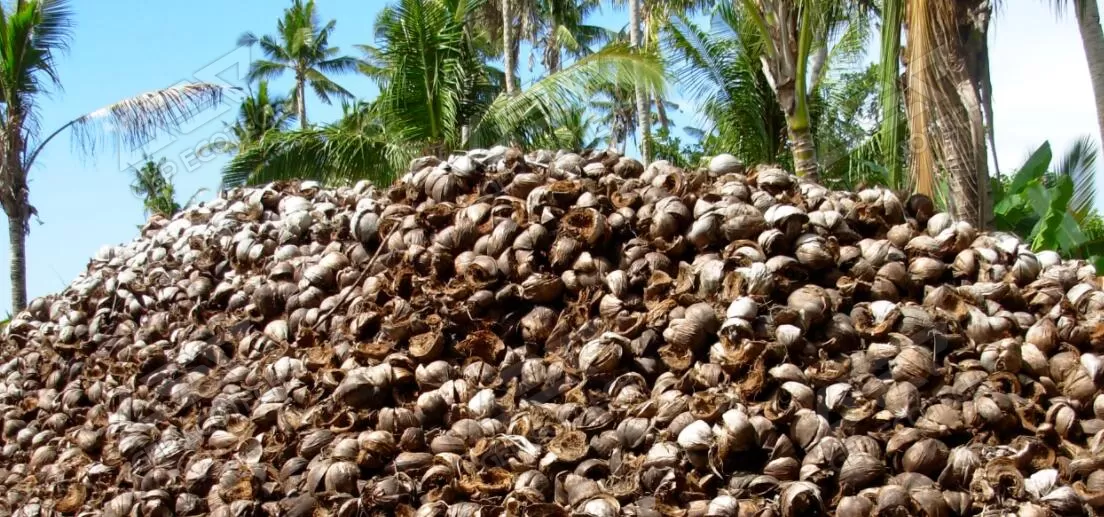

Every year tones of coconut shell and husk are being produced, though very small portions are being used in the field of feedstock and energy production. The expansion of bio-composites has amplified industrial usage that would release the possibilities to minimize the wastage of renewable materials. It promotes a non-food-based market for agricultural industry.
Coconut husk and shells are an attractive biomass fuel and are also a good source of charcoal. The major advantage of using coconut biomass as a fuel is that coconut is a permanent crop and available round the year so there is constant whole year supply. Activated carbon manufactured from coconut shell is considered extremely effective for the removal of impurities in wastewater treatment processes.
Coconut Husk Shredder Machine
GEP Ecotech GD range of slow speed, high torque waste shredders are probably the most flexible and functional slow speed shredder on the market today. Designed with strength, durability and serviceability in mind, our shredders can handle almost any material in any application. With a huge range of both rapid volume reduction and intricate piece sizing solutions available, our shredders can be employed as either a primary or secondary shredder and can be seen working anywhere from waste management companies to biofuel producers.
GEP Ecotech Shredders Suitable for Coconut Husk Process
Double Shaft Shredder GDB Series