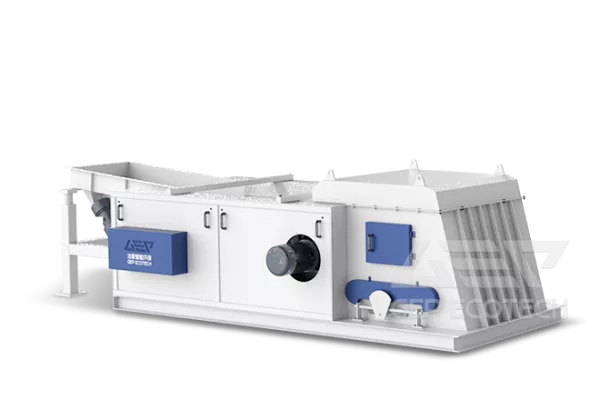
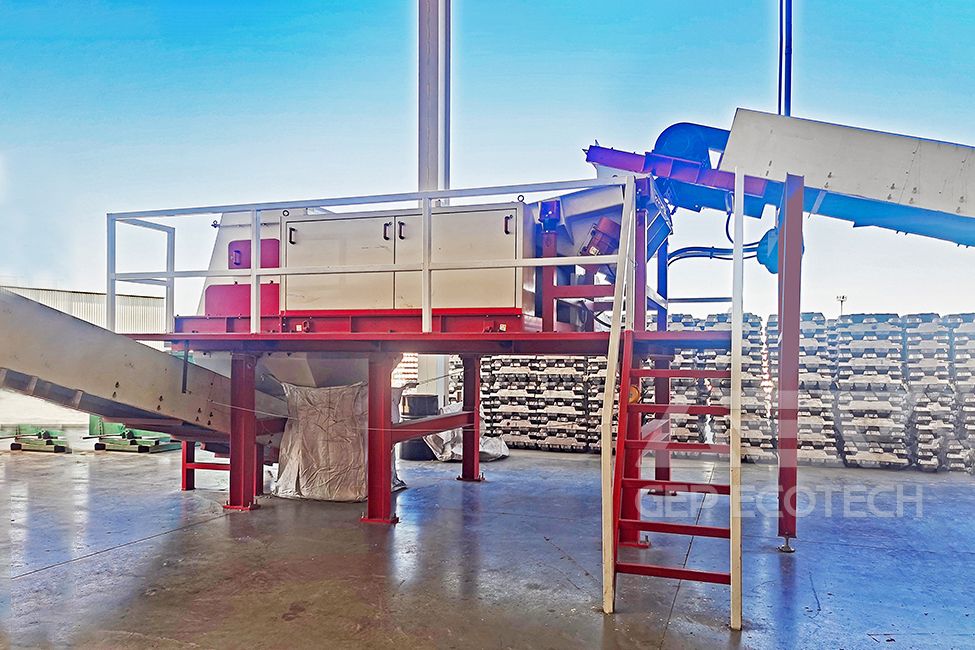
The structure of the eddy current separator includes the external drum and its driving motor, the internal magnetic roller and its driving motor, and the annular integrated belt. It is mainly used in industries such as selecting copper and aluminum from industrial waste, construction waste, and municipal solid waste (MSW), processing materials in non-ferrous metal processing, recovering copper, aluminum, and zinc from waste car fragments, recycling waste electrical appliances, removing aluminum rings from crushed glass, and other related copper and aluminum recycling industries.
After the equipment is turned on, the internal magnetic rollers run at high speed, and the conductors (non-ferrous metals) in the material generate induced currents in a high-frequency alternating magnetic field. The magnetic field generated by this current is opposite to the direction of the original magnetic field, producing a strong repulsive force on the non-ferrous metals, instantly ejecting them from the material, achieving the purpose of separation.